
Since the scientist is doing research for NASA with advanced Virtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence technologies, I had to find out about both these scientific topics. Since I wrote this a couple of years ago, it's probably out of date by now. And the book is no longer available, but I'm working to fix that..
WHAT IS VIRTUAL REALITY?
The Virtual Reality Society defines it this way.

We know the world, and our reality, through our senses and perception systems. In school we learned that we have five senses -- taste, touch, smell, sight and hearing -- but those are only our most obvious sense organs. The truth is, humans have many more senses than five, such as a sense of balance. These other sensory inputs, plus some special processing of sensory information by our brains, ensures that we have a rich flow of information from the environment to our minds.
Our entire experience of reality is simply a combination of sensory information and our brains sense-making mechanisms for that information. It stands to reason then, that if you can present your senses with made-up information, your perception of reality would also change in response to it. You would be presented with a version of reality that isn’t really there, but from your perspective it would be perceived as real. Something we would refer to as a virtual reality.
In summary, virtual reality entails presenting our senses with a computer generated virtual environment that we can explore in some fashion.
In technical terms "virtual reality” is straight-forward (Ha, ha, ha!.) and is the term used to describe a three-dimensional, computer generated environment which can be explored and interacted with by a person. That person becomes part of this virtual world or is immersed within this environment and, while there, is able to manipulate objects or perform a series of actions. In the last decade plus, our society has become familiar with the idea of virtual reality and getting "into" very complex, interactive video games which are very popular (to the tune of $60.4 billion dollars worldwide in 2009).
The beginnings of the concept date back to 1947 with the Cathode Ray Tube Amusement Device, the earliest known interactive electronic game. The term Virtual Reality was coined by Myron Krueger and has been in use since the 1970's, although it has been traced back to the French playwright Antonin Artaud in his book The Theater and Its Double (1938).
In the 21st century, there are many other applications of virtual reality in the fields of computer science, medicine, architecture, engineering, geology, oil exploration, business, military, entertainment, and the list goes on and on.
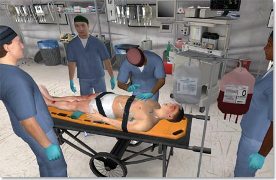
Parachute training Airplane trainer cockpit Medical simulator at Duke Teleconferencing
Virtual reality consists of a computer-generated, multi-dimensional environment that can simulate physical presence in places in the real world, as well as in imaginary worlds, and interface tools that allow human users to: 1) immerse themselves in the environment, 2) navigate within the environment, and 3) interact with objects and other inhabitants in the environment.
While virtual reality is a highly visual computer-generated, multi-dimensional environment experience, there are simulations which include sound, motion, vibration, tactile information, and other special effects to convey the sense of reality. In the book The Metaphysics of Virtual Reality by Michael R. Heim, seven different concepts of virtual reality are identified:1) Simulation, 2) Interaction, 3) Artificiality, 4) Immersion, 5) Telepresence, 6) Full-body immersion, and 6) Network communications.
Telexistence is the name for the general technology that makes it possible for a human being to experience a real-time sensation of being at a place other than where he/she actually exists physically, and being able to interact with the remote environment, which may be real, virtual, or a combination of both. It's just like being there.
So my human characters in All In The Game exist in a simulated world. No, really. They are physically there.

Artificial Intelligence ( or AI) isn't an idea generated by today's technology. The seeds of modern AI were planted by classical philosophers who attempted to describe the process of human thinking as the mechanical manipulation of symbols. This culminated in the invention of the programmable digital computer in the 1940s. This ultimately resulted in scientists seriously considering the possibility of a mechanical brain.

The Encyclopedia of Science and Religion defines Artificial Intelligence as "the field within computer science that seeks to explain and to emulate, through mechanical or computational processes, some or all aspects of human intelligence. Included among these aspects are the ability to interact with the environment through sensory means and the ability to make decisions in unforeseen circumstances without human intervention.
Typical areas of research in AI include game playing, natural language understanding and synthesis, computer vision, problem solving, learning and robotics. There is no agreed upon definition of artificial intelligence, primarily because there is little agreement as to what constitutes intelligence."

Humans have been interested in the process of thought for a long time, and the concept of artificial intelligence is based on the assumption that the process of human thought can be mechanized.The ancient Chinese, Indian, and Greek philosophers developed methods of formal deductive reasoning in the first millennium BC, and those methods were expanded further by Aristotle, Euclid, and others. The intellectual roots of AI and the concept of intelligent machines is found in Greek mythology.
While intelligent mechanical machine and robots have found their way into writing since the 13th century, it wasn't until after WWII, when modern computers became available, that it's been possible to design programs and build machine that perform difficult intellectual tasks.
Varying kinds and degrees of intelligence occur in people, many animals and some machines. There isn't a solid definition of intelligence that doesn’t depend on relating it to human intelligence because humans "cannot yet characterize in general what kinds of computational procedures we want to call intelligent. We understand some of the mechanisms of intelligence and not others."

All of us have seen and heard about complicated robots machines that build cars, harvest crops, and so on. Or the uses of Artificial Intelligence in the space program, such as the Mars Rover.
WHAT IS NANOTECHNOLOGY?
Oh, no! There's more? Yes, but just a few words.
Nanotechnology is the science and technology of building electronic circuits and machine from single atoms and molecules. Tiny machines! And when I say tiny, try to imagine that a nanometer is one billionth of a meter, roughly the width of three or four atoms. The average human hair is about 25,000 nanometers wide.
However, the technology is regarded now as a potential silver bullet for an array of global security challenges, concerns are also being raised as to what might happen should such technologies fall into the wrong hands.
Now, imagine what would happen if we combine artificial intelligence and nanotechnology.
Stop! You're scaring me!
□
Resources
Unfortunately, when I wrote the first version of this article, I didn't keep a list of the references. I have listed those I used to update the blog.
http://www.nanotech-now.com/current-uses.htm
http://www.crnano.org/overview.htm
https://www.technologyreview.com/s/533686/2014-in-computing-breakthroughs-in-artificial-intelligence/
https://www.technologyreview.com/s/513696/deep-learning/
http://www.2020research.com/virtual-reality/
http://news.stanford.edu/news/2011/april/virtual-reality-trees-040811.html
http://vhil.stanford.edu/
https://www.vrs.org.uk/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_artificial_intelligence
https://www.accenture.com/us-en/insight-artificial-intelligence-software
https://www.pega.com/ai-survey?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=900.Global-English.Active-Awareness&utm_term=artificial%20intelligence&gloc=9031315&utm_content=pcrid|192136514350|pkw|artificial%20intelligence|pmt|p|pdv|c|theme|rce&gclid=CMixv9






































































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed